Gastroenterology: Diagnosis and Treatment
Medical specialty interested in the study and treatment of diseases related to the digestive system
What is Gastroenterology ?
Gastroenterology is the specialty of medicine that studies the organs of the alimentary canal, their functioning and their pathologies. It treats various organs such as: the esophagus, the stomach, the small intestine, the large intestine, the rectum , The anus) and the digestive glands.
There are several specialties in gastroenterology including hepatology, proctology, the study and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases, ...
What are the services of the gastroenterology department ?
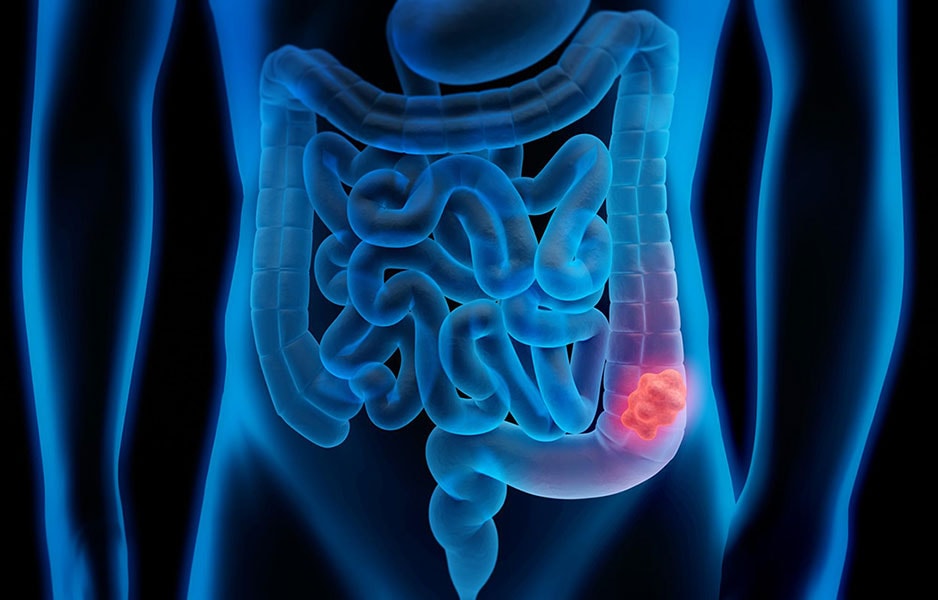
1. Colon cancer screening
colon cancer screening or colorectal cancer, is done via colonoscopy, which is the most important examination in the context of screening, it allows to highlight the polypes, which are small formations in the mucosa intestinal. Left untreated, these can progress to bowel cancer, which can be fatal.
2. The diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the esophagus and stomach
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the esophagus and stomach are made by the gastroenterologist. Following a consultation, the latter will decide whether or not to make an assessment of the disease, in this assessment there is the gastroscopy, blood test, ultrasound, etc.
What are the pathologies of the esophagus and stomach ?
The pathologies of the stomach and esophagus are diverse and all have specificities. It is important that you know the symptoms of each of these pathologies so that you can quickly turn to a gastroenterologist if you feel any of them.

- Esophagitis
Esophagitis is an inflammation of the mucosa in response to attacks. It is caused by gastroesophageal reflux or gastric reflux. It is often associated with an esophageal sphincter problem.
Indeed, the sphincter is located in the lower part of the esophagus. It is a muscle that plays the role of a valve and helps limit gastric reflux. So you can understand that a deficiency of this muscle leads to serious problems. The gullet is inflamed because of the acid that flows up the esophagus.
Here are the different esophagitis :
- Esophagitis caused by medication,
- Peptic esophagitis,
- Caustic esophagitis,
- Infectious esophagitis.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux is nothing more than the return of stomach contents into the esophagus namely bile (from the gallbladder) and acid. This dysfunction causes inflammation of the esophagus and severe pain in the lower chest. This condition is common in both infants and adults.
- Esophageal ulcer
With symptoms such as heartburn, indigestion, abdominal cramps, esophageal inflammation, etc., esophageal ulcer is caused by: gastroesophageal reflux, bacterial or mycotic infection, or necrotizing esophagitis.
This condition can also be caused by improper absorption of a medication. In addition, diet, alcohol and smoking can also be the cause of an esophageal ulcer.
- Esophageal infections
Esophageal infections occur in people whose defense mechanisms are not in good shape (deficient). The most common causes are cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus and candida albicans infections.
- Gastric motility disorders
Gastric motility disorders include gastroparesis, paralytic ileus, intestinal peristalsis pathology, esophageal achalasia, etc. They represent a dysfunction of the esophagus that causes heartburn, chest pain and dysphagia.
- Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the stomach lining. It is caused by various factors such as stress, injuries, medications, immune system disorders. The symptoms of this condition are pain or discomfort in the stomach. Vomiting and nausea can sometimes occur.
- Gastric ulcer
Still called peptic ulcer, gastric ulcer is a set of wounds that enter the wall of the digestive tract. These sores hurt a lot because they are in direct contact with the acid in the digestive tract. The pain is similar to that felt when alcohol is applied to a scratch.
- Stomach tumors
Tumors of the stomach are divided into two types. They are non-cancerous stomach tumors and cancerous stomach tumors. Non-cancerous or benign tumors are a mass that grows into other organs of the body. They are not life-threatening. Treatment is surgical.
Cancerous tumors of the stomach are malignant tumors. This is called stomach cancer. It originates in the gastric wall at the level of the inner lining. It grows, invades the wall, and may invade nearby organs.
3. Food intolerances
In front of any suspicion of a food intolerance, following a consultation, the specialist in charge of your medical file will ask you to do special tests which are done within the clinic, the result is communicated to the gastroenterologist, who will then make a diagnosis and give treatment adapted to the problem.
4. Diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease
These are chronic diseases of unknown origin, which are diagnosed and treated by the gastroenterologist during a consultation and colonoscopy, after which treatment is initiated with regular support for evaluation and disease surveillance.
5. Digestive Endoscopy
Endoscopic examination by means of a camera of the lower and upper digestive tract, it is done on an empty stomach. The examination of the lower digestive tract is done after a preliminary preparation and a diet without fiber.
What tests are performed in gastroenterology ?
When you go to the gastroenterology center, various types of tests are performed depending on the pathology you have. These examinations allow for specific patient care to be tailored as needed. Indeed, through these examinations, doctors mainly look for polyps or cancerous tumors; they also look for inflammatory diseases or growths that could become malignant. Here are some of these examinations in detail !

1 - Colonoscopy
Colonoscopy is an endoscopic examination that consists of the visualization of the internal wall of the colon. This examination is performed by a device called a colonoscope, which consists of a thin flexible tube connected to a cold light source and a small camera.
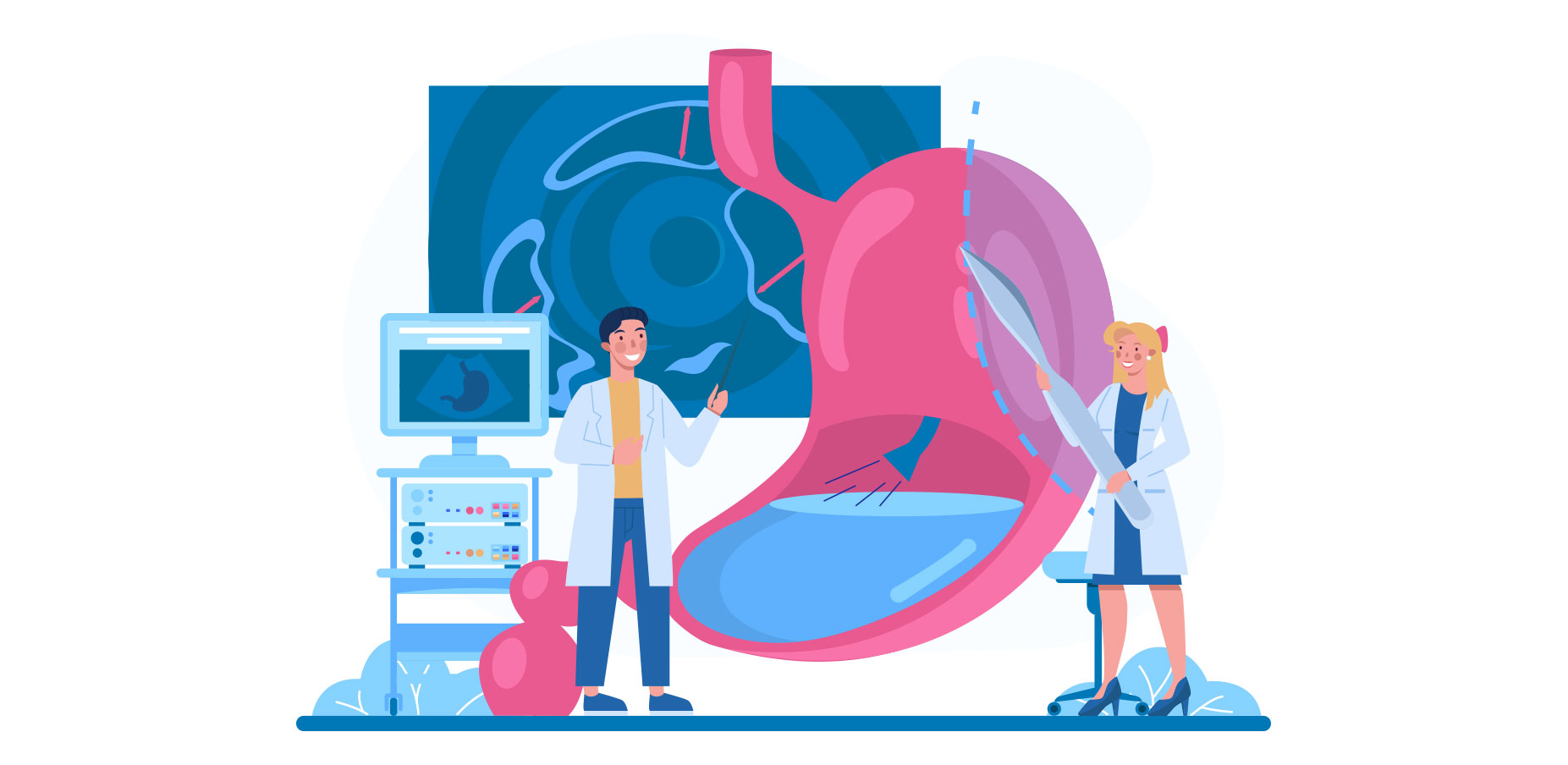
2 - Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy is an examination to visualize the inner lining of the esophagus, stomach and duodenum. This procedure allows you to see inside the organs with a flexible tube connected to a light source and a small camera called a gastroscope.
3 - Esophageal Manometry
Esophageal manometry is an examination that provides information about the functioning of the esophagus contraction. A recording is made of the internal pressure along the esophagus with a special probe. This examination is not painful.
4 - Anorectal manometry
Anorectal manometry is an examination that explores the functioning of the contraction of the rectum and the anal canal, thus allowing the recording of the internal pressure. It allows us to know the precise cause of the symptoms you are experiencing. This examination is not painful.
5 - Colo-scanner
The colo-scanner or virtual coloscopy is a method that allows the exploration of the colon by a scanner. It follows precise criteria for analysis and realization. It is used when it is impossible to perform a colonoscopy.
6 - BTU
The Breath Test with Urea is an examination which allows to search for the presence of a bacterium (Helicobacter Pylori) in the mucous membrane of the stomach. The BTU test is performed on the patient's exhaled air and is non-invasive and non-radioactive.
7 - BTL
The lactose intolerance test or breath hydrogen test is a breath test that allows the evaluation of the intestinal digestion of lactose.
What is the role of the gastroenterologist ?

A gastroenterologist is a physician who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive system. He treats various health problems related to the digestive system such as ulcers, Crohn's disease, gastric cancers, hemorrhoids, gallstones, cirrhosis, etc.
The gastroenterologist prevents, detects and treats digestive diseases
A gastroenterologist is a practitioner whose role is to screen for diseases related to the digestive system, regardless of the patient's age. In people over the age of 50, he or she provides screening for colorectal cancers. In addition, it is also active in prevention. That is, he helps patients to have the right behaviors such as a good diet and quitting smoking and alcohol.
When should I see a gastroenterologist?
It is important to consult a gastroenterologist if you experience any of the following symptoms: chest or abdominal pain (could indicate a disease of the digestive system), nausea, vomiting, a feeling of regurgitation or acidity, at the slightest bleeding, etc.
To make an appointment with a gastroenterologist, you can contact our gastroenterology center which is located in the heart of Brussels, at 90, avenue du bois de la Cambre, in Ixelles.


